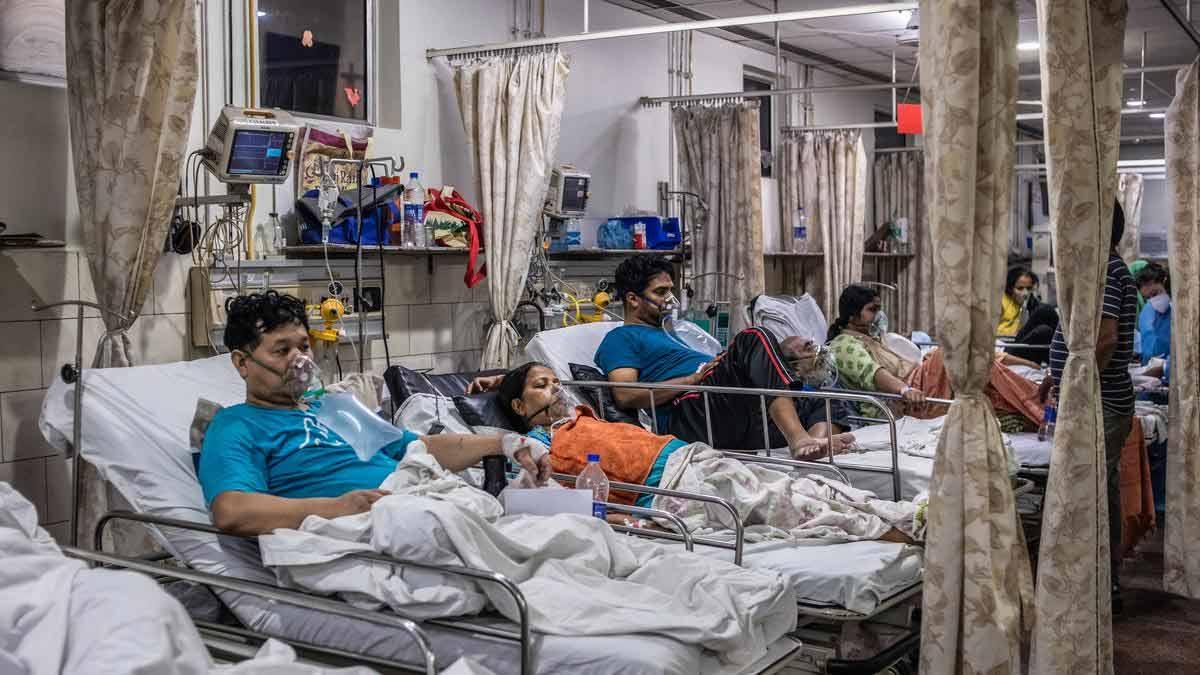
A research conducted by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) found some contributing factors—such as past hospitalisation for severe Covid-19, family history of sudden fatalities, and a few lifestyle habits—as probable causes for sudden, unexplained young adult deaths in India.
Reported in the Indian Journal of Medical Research, peer-reviewed research considered risk factors associated with sudden deaths in adults aged 18 to 45.
Contrary to rumors in the public sphere, it discovered no association between Covid-19 vaccination and sudden deaths.
Carried out in 2023, the study was prompted by extensive anecdotal evidence indicating that unexplained sudden death among apparently healthy young people could be linked to either Covid-19 infection or vaccination.
"Covid-19 vaccination did not raise the risk of unexplained sudden death among young adults in India. History of previous Covid-19 hospitalisation, personal history of sudden death, and some lifestyle behaviors made unexplained sudden death more likely," the scientists noted.
The research employed a multicentric matched case-control design and consisted of 729 cases and 2,916 controls from 47 tertiary hospitals nationwide. The cases were adults aged between 18 and 45 years with no known co-morbidities who suddenly died without any known cause despite showing no apparent indication of illness just 24 hours prior to their death between October 2021 and March 2023.
Every case was paired with four controls from the same age, gender, and residential area.
Data was collected using interviews and hospital records in-depth to study such factors as Covid-19 vaccine and infection history, post-Covid complications, sudden death family history, smoking, alcohol, binge drinking, drug use, and strenuous exercise in the 48 hours preceding death or interview.
The findings indicated that one or more doses of Covid-19 vaccine reduced the risk for sudden unexplained death," the scientists added. Taking two doses reduced the risk further.
But other factors like history of hospitalisation due to Covid-19, sudden death in families, binge drinking, consumption of recreational drugs, and high-intensity sport activity within two days of death were all linked with a greater chance of sudden, unexpected death, the research found.
Read also| Is Online Physiotherapy Effective? Expert Advice and Patient Reviews
Read also| “Live 200 Years”: Ramdev Sparks Anti-Ageing Debate After Shefali Jariwala’s Death