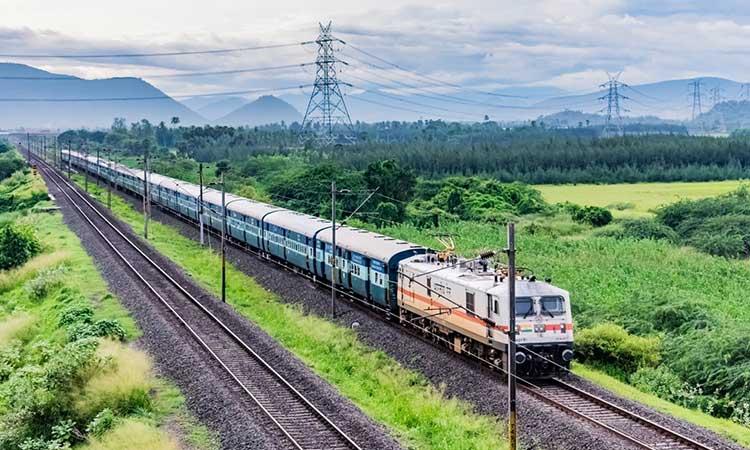
The Indian Railways is one of the largest and oldest railway networks in the world, connecting every corner of the country with its vast and diverse geography. The history of the Indian Railways is a story of innovation, transformation, and modernization, from the era of steam engines to the advent of bullet trains.
Here is an overview of the evolution of the Indian Railways:
● The first passenger train in India ran on 16 April 1853, between Bori Bunder (Mumbai) and Thane, covering a distance of 34 km with 14 coaches and 400 passengers. It was operated by the Great Indian Peninsula Railway (GIPR) and hauled by three steam locomotives (Sahib, Sindh, and Sultan). This marked the beginning of rail transport in India.
● The first railway proposals for India were made in 1832, but it took two decades for the British government to approve them. The first railway lines were built by private companies, mostly for transporting goods and military personnel. By 1860, there were about 9,000 km of railway lines in India, connecting major cities like Kolkata, Delhi, Chennai, and Mumbai.
● The Indian Railways was formed by amalgamating 42 railways owned by the former Indian princely states after independence in 1947. The network stood at 55,000 km after independence. India inherited a decrepit rail network that needed substantial improvement. Many lines were re-routed and new lines were constructed to connect important cities and regions.
● The first electric train in India ran on 3 February 1925, between Bombay Victoria Terminus and Kurla Harbour. The first diesel train in India ran on 18 January 1950, between Delhi and Jaipur. In 1952, the existing rail networks were divided into six zones for administrative purposes. In 1985, steam locomotives were phased out and electric and diesel locomotives took their place.
● The first computerised reservation system in India was introduced in 1986 at New Delhi. The Passenger Name Record (PNR) system was introduced in 1996 to enable passengers to check their reservation status online. The online ticket booking facility was launched in 2002 through the IRCTC website.
● The first metro rail service in India started in Kolkata in 1984. It was followed by Delhi Metro in 2002, which is now the largest metro network in India. Other cities like Bengaluru, Chennai, Hyderabad, Mumbai, and Kochi also have metro rail services. Metro rails provide fast and convenient urban transport for millions of commuters.
● The first high-speed rail project in India is the Mumbai-Ahmedabad bullet train corridor, which is expected to be completed by 2023. It will reduce the travel time between the two cities from eight hours to two hours. The bullet train will run at a speed of 320 km/h on a dedicated track of 508 km. It is being developed with the assistance of Japan.
● The Indian Railways has also undertaken several initiatives to improve its safety, efficiency, and sustainability. Some of these include introducing bio-toilets in coaches, installing CCTV cameras and GPS devices in trains, implementing automatic train protection systems, electrifying the entire rail network by 2023-24, and becoming a "net-zero carbon emitter" railway by 2030.
The Indian Railways has come a long way since its inception and has played a vital role in the economic and social development of the country. It is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs and expectations of its passengers and stakeholders. It is a symbol of national pride and integration for millions of Indians.
To explore the extensive Indian railway network, it is advisable to make advance reservations, commonly referred to as railway reservation bookings. Railway reservation is the process of booking a seat or berth on a train for travelling from one station to another. Railway reservation can be done online or offline, depending on the convenience and preference of the passenger. Online railway reservation is done through websites like redRail or apps that are authorised by Indian Railways to provide this service. Offline railway reservation is done by visiting the railway station booking window or authorised agents.
Once you've made a reservation for your train ticket, you can monitor its status using the PNR number by PNR enquiry. PNR enquiry is the process of checking the current status of a reserved railway ticket. PNR stands for Passenger Name Record, which is a unique 10-digit number that is printed on the ticket. PNR enquiry can be done online or offline, depending on the availability and accessibility of the passenger. Online PNR enquiry is done through websites or apps that are authorised by Indian Railways to provide this service. Offline PNR enquiry is done by calling the railway enquiry number 139 or sending an SMS to 139 or 5676747.
Whether you're looking to book railway reservations or check PNR status, you can do it all on a single website called redRail. redRail is an online railway ticket booking platform that is powered by redBus, a leading online bus ticket booking service. redRail is an IRCTC-authorised partner that allows passengers to book train tickets for their preferred trains in just a few minutes. redRail also provides features such as live train running status, train schedule, seat availability, fare enquiry, and instant refund on UPI payments. redRail aims to make the train ticket booking process smooth and hassle-free for the passengers.