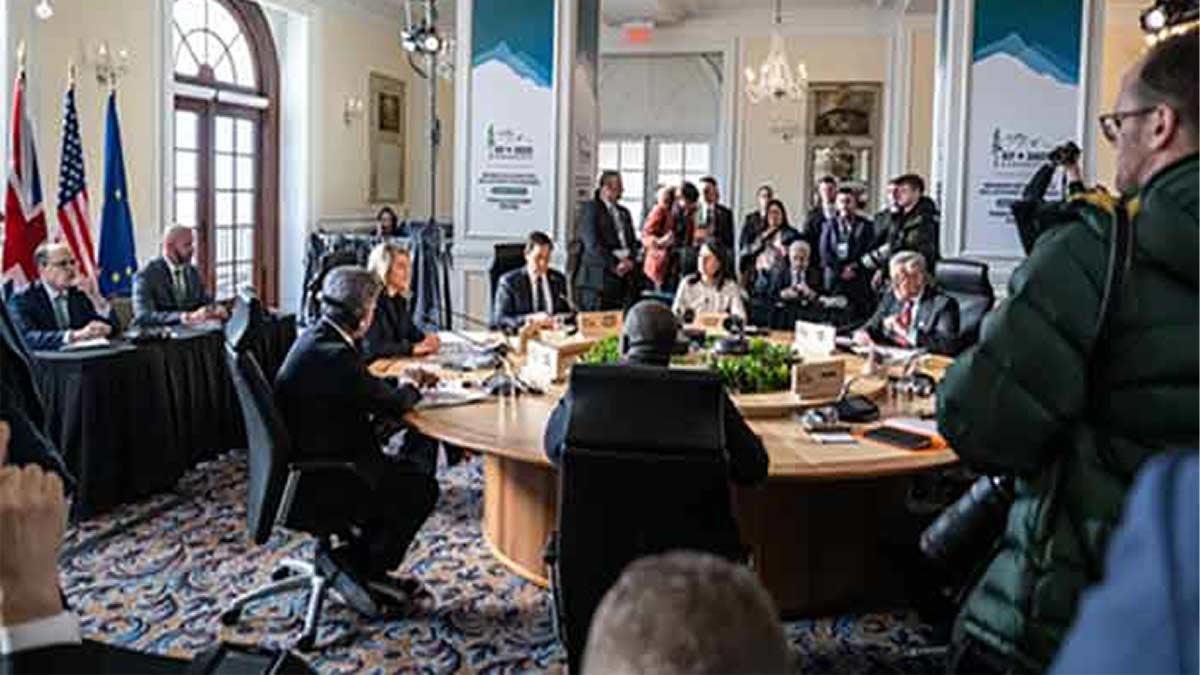
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has painted an optimistic picture of the Indian economy, forecasting a robust GDP growth of 7 percent for the fiscal year 2024-25, in its latest annual report released on Thursday. India's economy was able to post a 7.6 percent growth last fiscal in the face of challenges in the global economy and facing various impediments.
In fact, it was the third consecutive year of growth at 7 percent or higher, reflecting sustained momentum. The report further said this was underpinned by continued strengthening of macroeconomic fundamentals, buoyant financial and corporate sectors, and resilience in the external sector, which have been the drivers of growth going into the next fiscal.
The government's commitment to stepping up capital expenditure with fiscal prudence, along with upbeat consumer and business sentiments, augurs well for both investment and consumption demand, it added. The prospects of the agriculture and rural sector also look promising, with the El Nino impact dying down and the assumption of an above-normal southwest monsoon.
Also, the extension of the scheme Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY) for five years commencing from January 1, 2024, is expected to be a major step toward strengthening national food security. Other initiatives under AatmaNirbhar Oilseeds Abhiyan, in addition to efforts for promoting environment-friendly farming practices, including nano diammonium phosphate (DAP) use in diverse agro-climatic zones, augur well for the agriculture sector.
In this regard, schemes proposed in the interim Union Budget 2024-25, such as bio-manufacturing and bio-foundry scheme, reflect the interest of the government toward the bioeconomy and its commitment to growth that is sustainable. In the next fiscal year, the capital spending of the central government is set to continue unabated, and a major share of its borrowings is going toward financing the capital outlay.
Meanwhile, the extension of the financial assistance scheme for states' capital expenditure up to 2024-25, at an outlay of Rs 1.3 lakh crore, is bound to give yet another impetus to growth. Besides, gross market borrowings are expected to decline from 5.3 percent of GDP in the previous fiscal to 4.3 percent in 2024-25, releasing space for financing of the private sector and supporting private investments.
Read More | Significant RBI Dividend to Government Viewed Positively for India's Rating by Fitch
Read More | Government to Auction Rs 29,000 Crore in Bonds on May 31