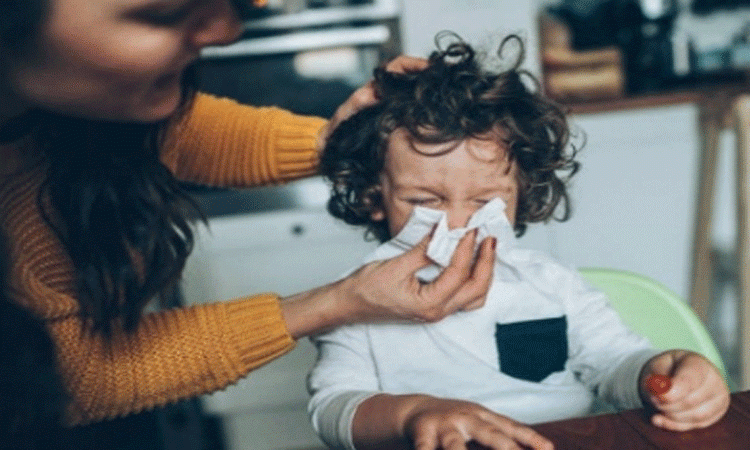
Children infected with seasonal common cold are likely to have immunity against Covid-19, according to a research.
During the pandemic, medical doctors and researchers noticed that children and adolescents infected with Covid became less ill than adults.
To understand this, researchers from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, studied unique blood samples from children taken before the pandemic.
They identified memory T cells that react to cells infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid.
Also read |Covid-19 can cause 'face blindness': Study
A possible explanation for this immunity in children is that they already had colds caused by one of the four coronaviruses causing seasonal common cold symptoms, the researchers said.
This new study reinforces this hypothesis and shows that T cells previously activated by the OC43 virus can cross-react against SARS-CoV-2.
"These reactions are especially strong early in life and grow much weaker as we get older," said corresponding author Annika Karlsson, research group leader at the Department of Laboratory Medicine, Karolinska Institutet.
"Our findings show how the T-cell response develops and changes over time and can guide the future monitoring and development of vaccines."
Also read |H3N2 virus: Health experts call for masks, better hygiene & flu shot
The study is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The results indicate that the memory T-cell response to coronaviruses develops as early as the age of two.
The study was based on 48 blood samples from two- and six-year-old children, and 94 samples from adults between the ages of 26 and 83.
The analysis also included blood samples from 58 people who had recently recovered from Covid.
"Next, we'd like to do analogous studies of younger and older children, teenagers and young adults to better track how the immune response to coronaviruses develops from childhood to adulthood," said Marion Humbert, postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Medicine Huddinge, Karolinska Institutet.