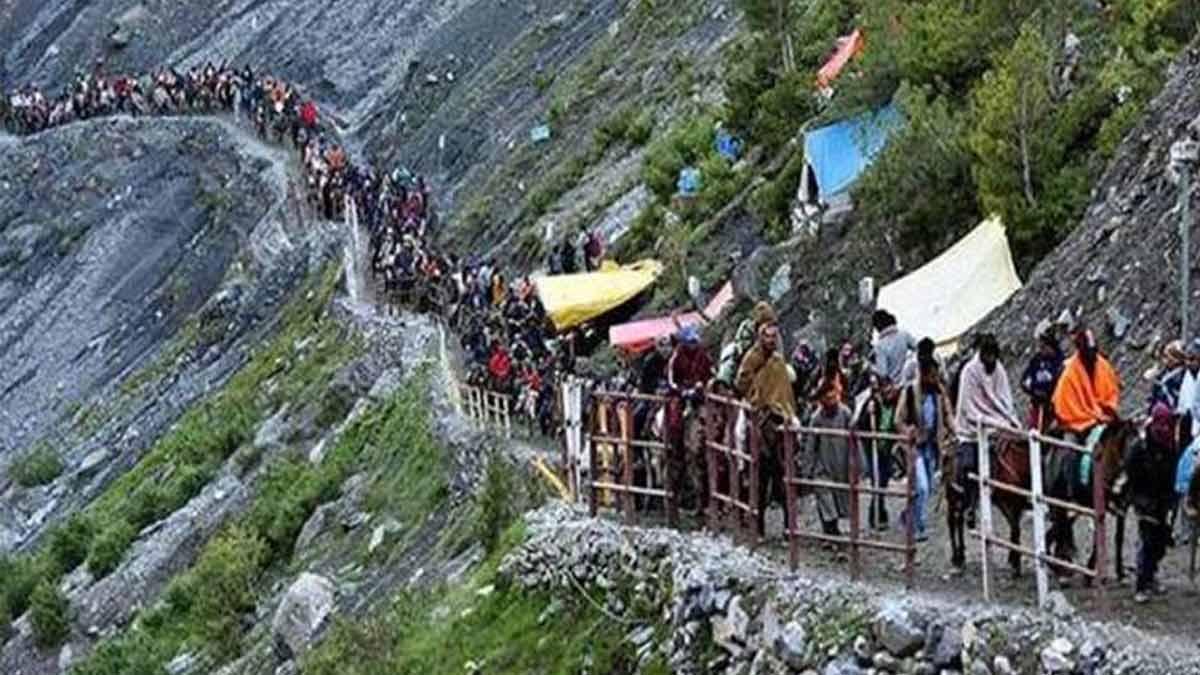
The Supreme Court on Wednesday upheld the validity of Section 19 of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), which postulates the manner of arrest of a person involved in money laundering, saying that safeguards are provided in the Act and the preconditions to be fulfilled by the authorised officer before effecting arrest, are equally stringent and of higher standard.
A bench, headed by Justice A.M. Khanwilkar and comprising Justices Dinesh Maheshwari and C.T. Ravikumar said: "We have no hesitation in upholding the validity of Section 19 of the 2002 Act. We reject the grounds pressed into service to declare Section 19 of the 2002 Act as unconstitutional."
The bench added that such a provision has reasonable nexus with the purposes and objects sought to be achieved by the Act of prevention of money laundering and confiscation of proceeds of crime involved in money laundering, including to prosecute persons involved in the process or activity connected with the proceeds of crime.
The PMLA is a comprehensive legislation, not limited to provide for prosecution of persons involved in the offence of money laundering, but mainly intended to prevent money laundering activity and confiscate the proceeds of crime involved in money laundering, it said.
The bench added that this legislation is an amalgam of different facets including setting up of agencies and mechanisms for coordinating measures for combating money laundering.
"It is not as if after every inquiry, prosecution is launched against all persons found to be involved in the commission of offence of money laundering. It is also not unusual to provide for the arrest of a person during such inquiry before filing of a complaint for indulging in alleged criminal activity," it noted.
The top court said it is, thus, obliging the person to be obedient to law. "The safeguards provided in the 2002 Act and the preconditions to be fulfilled by the authorised officer before effecting arrest, as contained in Section 19 of the 2002 Act, are equally stringent and of higher standard," added the bench, in its 545-page judgment.
Also Read | Pakistan Taliban don't trust Pakistani ulema in the absence of military assurance
The top court said safeguards ensure that the authorised officers do not act arbitrarily, but make them accountable for their judgment about the necessity to arrest any person as being involved in the commission of offence of money laundering even before filing of the complaint before the special court under Section 44(1)(b) of the 2002 Act.
"Suffice it to observe that this power has been given to the high-ranking officials with further conditions to ensure that there is objectivity and their own accountability in resorting to arrest of a person even before a formal complaint is filed under Section 44(1)(b) of the 2002 Act.
"Investing of power in the high-ranking officials in this regard has stood the test of reasonableness."
The top court clarified that the authorities under the 2002 Act are not police officers.
"Ex-consequenti, the statements recorded by authorities under the 2002 Act, of persons involved in the commission of the offence of money laundering or the witnesses for the purposes of inquiry/investigation, cannot be hit by the vice of Article 20(3) of the Constitution or for that matter, Article 21 being procedure established by law," it added.
The bench noted that in a given case, whether the protection given to the accused who is being prosecuted for the offence of money laundering, of Section 25 of the Evidence Act is available or not, may have to be considered on a case-to-case basis being the rule of evidence.
The petitioners had argued that the procedure being followed under the PMLA is draconian as it violates the basic tenets of the criminal justice system and the rights enshrined in Part III of the Constitution, in particular Articles 14, 20 and 21.
Not mandatory for ED to supply ECIR, disclosing ground of arrest enough: SC
The Supreme Court on Wednesday said supply of a copy of Enforcement Case Information Report (ECIR) in every case to the person concerned is not mandatory, while holding it is not equivalent to an FIR.
A bench, headed by Justice A.M. Khanwilkar and comprising Justices Dinesh Maheshwari and C.T. Ravikumar said: "Supply of a copy of ECIR in every case to the person concerned is not mandatory, it is enough if ED at the time of arrest, discloses the grounds of such arrest."
The bench said in view of a special mechanism envisaged by the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), the ECIR cannot be equated with an FIR. "ECIR is an internal document of the ED and the fact that FIR in respect of scheduled offence has not been recorded does not come in the way of the authorities referred to in Section 48 to commence inquiry/investigation for initiating 'civil action' of 'provisional attachment' of property being proceeds of crime," it added.
It said the argument of prejudice pressed into service by the petitioners for non-supply of ECIR deserves to be answered against the petitioners. "For, the arrested person for offence of money laundering is contemporaneously informed about the grounds of his arrest; and when produced before the Special Court, it is open to the Special Court to call upon the representative of the ED to produce relevant record concerning the case of the accused before him and look into the same for answering the need for his continued detention," it added.
The petitioners' counsel had argued that as per present situation, the ED can arrest an individual on the basis of an ECIR without informing him of its contents, which is per se arbitrary and violative of the constitutional rights of an accused. It was vehemently argued that in some cases, the ECIR is voluntarily provided, while in others it is not, which is completely arbitrary and discriminatory.
Senior advocate Kapil Sibal, representing one of the petitioners, while referring to the definition of "money laundering" under Section 3 of the PMLA, submitted that the ED must satisfy itself that the proceeds of crime have been projected as untainted property for the registration of an ECIR or the application of the PMLA.
The top court said that ECIR cannot be equated with an FIR which is mandatorily required to be recorded and supplied to the accused. "Revealing a copy of an ECIR, if made mandatory, may defeat the purpose sought to be achieved by the 2002 Act including frustrating the attachment of property (proceeds of crime)," it said.
It held that non-supply of ECIR, which is essentially an internal document of the ED, cannot be cited as violation of constitutional right. "This is compliant with the mandate of Article 22(1) of the Constitution. It is not unknown that at times FIR does not reveal all aspects of the offence in question. In several cases, even the names of persons actually involved in the commission of offence are not mentioned in the FIR and described as unknown accused," it noted.
Also Read | Nawaz Sharif wants early elections
The bench said even, the particulars as unfolded are not fully recorded in the FIR, despite that, the accused named in any ordinary offence is able to apply for anticipatory bail or regular bail, in which proceeding, the police papers are normally perused by the court concerned.
It also noted that in some cases, the ED has furnished a copy of ECIR to the person before filing of the complaint. "That does not mean that in every case the same procedure must be followed. It is enough, if the ED at the time of arrest, contemporaneously discloses the grounds of such arrest to such person," it said.
The top court noted that ECIR may contain details of the material in possession of the authority and recording satisfaction of reason to believe that the person is guilty of money laundering offence. "If revealed before the inquiry/investigation required to proceed against the property being proceeds of crime including to the person involved in the process or activity connected therewith, may have deleterious impact on the final outcome of the inquiry/investigation," said the bench.
The ED had submitted that the ECIR is an internal document created by the department before initiating penal action or prosecution against the person involved with process or activity connected with proceeds of crime.
The top court judgment came on more than 200 petitions challenging various provisions of the PMLA.