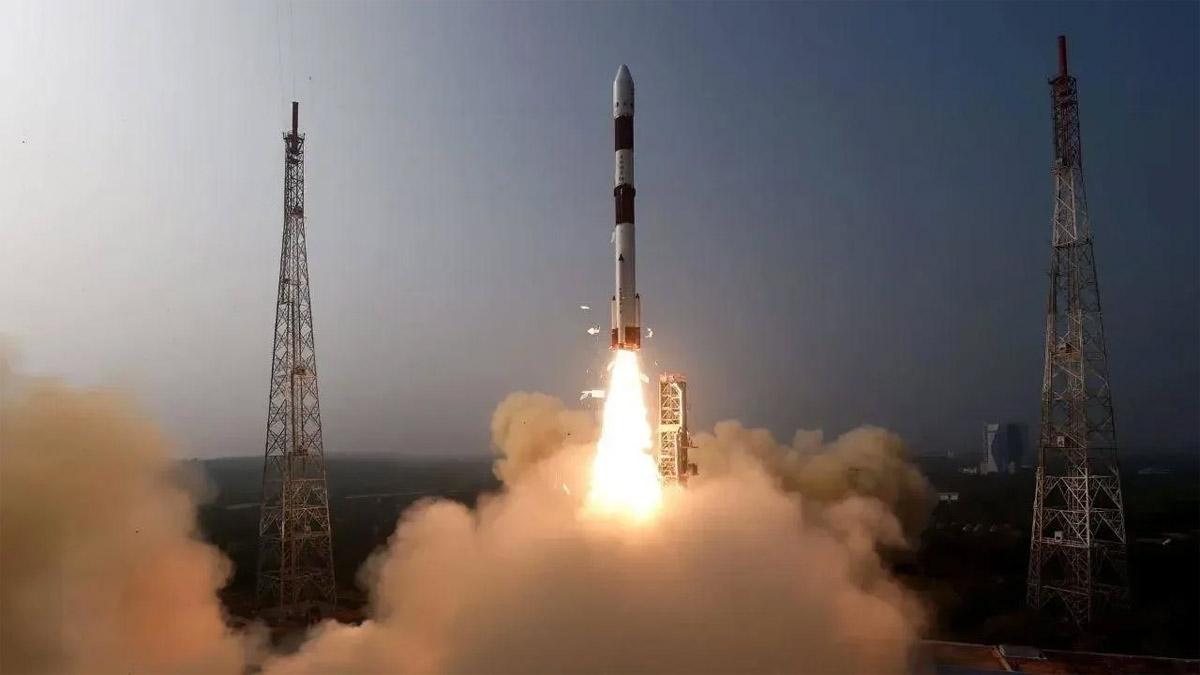
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has declared that the lift-off for the expected launch of PSLV-C59/PROBA-3 mission satellites will take place on December 4 (Wednesday), at 4:06 p.m. from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh.
The mission will involve carrying around satellites weighing nearly 550 kg in a highly elliptical orbit by the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV)-C59.
It is the European Space Agency (ESA's) In-Orbit Demonstration (IOD) mission: PROBA-3.
On X, the space body announced with a posting: "PSLVC59/PROBA-3 Mission-The 61st flight of PSLV and the 26th with the PSLV-XL configuration-is slated to carry ESA's PROBA-3 satellites (~550kg)-for a highly elliptical orbit."
According to ISRO, in the launch release, the goal is for the demonstration of accurate formation flying.
The mission comprises two spacecraft: the Coronagraph Spacecraft (CSC) and the Occulter Spacecraft (OSC), which are to be launched together in a "stacked configuration" of one on top of the other.
PSLV is a launch vehicle that helps carry satellites and many other payloads to space, according to ISRO requirements. PSLV is the first Indian vehicle to have liquid stages.
The first PSLV launched in October 1994 successfully.
According to ISRO, PSLVC-59 is a four-stage launch.
The total mass being taken off with this launch vehicle is roughly about 320 tonnes.
It also explained how this launch mission, in a way, marks the "trusted precision" of PSLV and collaboration between the space organization and other agencies.
This is, he wrote in his post, an "exemplary proof of the trusted precision of PSLV and cooperation between NSIL (NewSpace India Limited), ISRO and ESA".
The last mission using PSLV was PSLV-C58 launching XPOSAT satellite to an "Eastward low inclination orbit on January 1, 2024".
The Proba-3 mission of the European Space Agency, according to their announcement, is "world's first precision formation flying mission". It is scheduled to explore the outermost layer and the hottest portion of the Sun's atmosphere known as the corona.
The satellite was also named as the Xray Polarimeter Satellite. It is the country's first dedicated scientific satellite from ISRO, toward carrying out research in space-based polarisation measurements of X-ray emission from celestial sources.
Read also| India Set to Sign Deal for 26 Rafale-M Jets Soon: Navy Chief