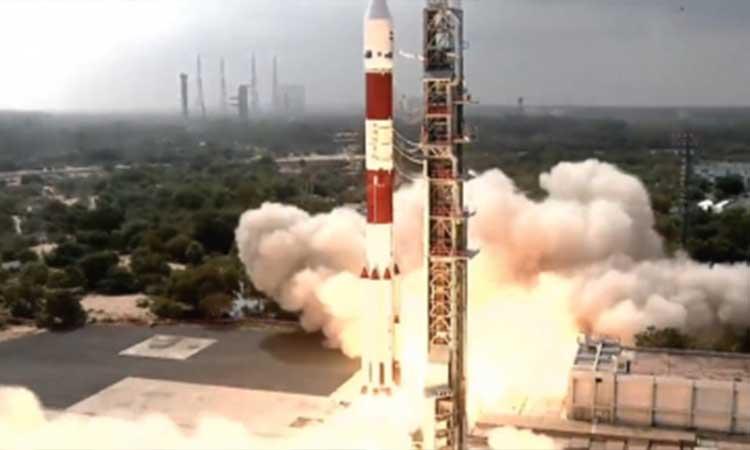
India on Saturday successfully placed into orbit the Indo-French ocean observation satellite EOS 6 with its rocket Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle numbered as PSLV-C54.
The process of orbiting eight other nanosatellites piggybacking is underway and officials of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) said it would happen smoothly as planned.
Speaking to the media after the successful launch of EOS 6, ISRO Chairman and Secretary, Department of Space, S. Somanath, said: "Happy to announce the successful mission. The satellites solar panel has been deployed.
He added that the satellite was orbited in precise orbit as intended and congratulated the team.
Also read | 26/11 attacks: Maharashtra remembers martyrs, victims, survivors
Somanath said the mission is yet to be completed as the rocket will have to be brought down to a lower orbit to eject the other satellites.
The XL variant of PSLV rocket carrying the 1,117 kg EOS-6 as its primary passenger and eight others- blasted off from the first launch pad at Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) here at 11.56 a.m.
The piggybacks include satellites from two Indian startups - Syzygy Space Technologies Pvt Ltd, commonly known as Pixxel (Anand-16.51 kg), and Dhruvaspace's two Thybolt satellites - 1.45 kg, Spaceflight USA's Astrosat (four numbers 17.92 kg) and ISRO's INS-2B (18.28 kg).
About 17 minutes into the flight the rocket ejected EOS-6. Then the orbit will be changed by using two Orbit Change Thrusters
introduced in the rocket's propulsion bay ring. The piggyback passengers will be separated in Orbit-2.
If all goes well, the PSLV rocket would orbit 349 foreign satellites till date.
When one takes into account the 36 satellites of UK based OneWeb that were orbited by another rocket LVM3 this year, then the total number of foreign satellites put into orbit by ISRO would go up to 381.
At the end of the final countdown, the four stage expendable, 44.4 m tall XL variant of PSLV rocket weighing 321 ton slowly rose towards the skies with thick orange flame at its tail.
The rocket gained speed as it went up while emitting a rolling thunder sound.
The PSLV rocket is powered by solid (first and third stages) and liquid (second and fourth stages) fuels alternatively.
The rocket that flew on Saturday was the 56th mission of PSLV and 24th mission using the PSLV-XL variant having six strap-on booster motors with six ton fuel.
The ISRO said the Indo French collaborative EOS-6/Oceansat will provide continuity services of Oceansat-2 spacecraft with enhanced
payload capabilities and application areas.
The EOS-6 payloads include Ocean Color Monitor (OCM-3), Sea Surface Temperature Monitor (SSTM), Ku-Band Scatterometer (SCAT-3) and ARGOS - a French payload.
According to France, ARGOS will reinforce the existing fleet of Indo-French satellites working on weather surveillance that are
already in orbit (MEGHA-TROPIQUES and SARAL-ALTIKA), thus enhancing contributions related to the objectives of the Paris Agreement.
The Indian space agency said the satellite will ensure data continuity of ocean colour and wind vector data to sustain the operational applications. It will also improve the applications, some additional datasets such as Sea Surface Temperature and more bands in Optical region for fluorescence and in Infrared region for atmospheric corrections are accommodated.
The satellite will also develop/improve related algorithms and data products to serve in well established application areas and to enhance the mission utility.
The INS-2B is ISRO's second nano satellite for Bhutan with two payloads viz., NanoMx and APRS-Digipeater. The NanoMx is a
multispectral optical imaging payload developed by its Space Applications Centre (SAC). The APRS-Digipeater payload is jointly
developed by DITTBhutan and ISRO's UR Rao Satellite Centre (URSC), ISRO said.
The Pixxel's Anand nanosatellite is a technology demonstrator to demonstrate the capabilities and commercial applications of
miniaturized earth-observation camera for earth observation using a microsatellite in Low Earth Orbit. This is a three-axis stabilised satellite consisting of a satbus, accommodating all subsystems like telemetry, tele-command, electrical power system, Attitude Determination and Control System (ADCS), on-board computers and others and a payload unit, ISRO said.
Also read | No institution is perfect in a Constitutional democracy: CJI
The Dhuruvaspace's Thybolt satellites have a communication payload to enable rapid technology demonstration and constellation development for multiple users. It also demonstrates Store-and-Forward functionality for authorised users in the amateur frequency band.
The two satellites shall be deployed by using Dhruva Space Orbital Deployer to perform the specific mission operations for a minimum
lifetime of one year.
Astrocast, a 3U spacecraft, is a technology demonstrator satellite for the Internet of Things (IoT) as the payload.